Panorama Stitching with ORB/SIFT Features
Panorama stitching involves joining images taken at different angles. This is nontrivial since it’s challenging to line them up. By using ORB features (key landmarks), one can use this to find the affine mapping related to the two images as shown below. 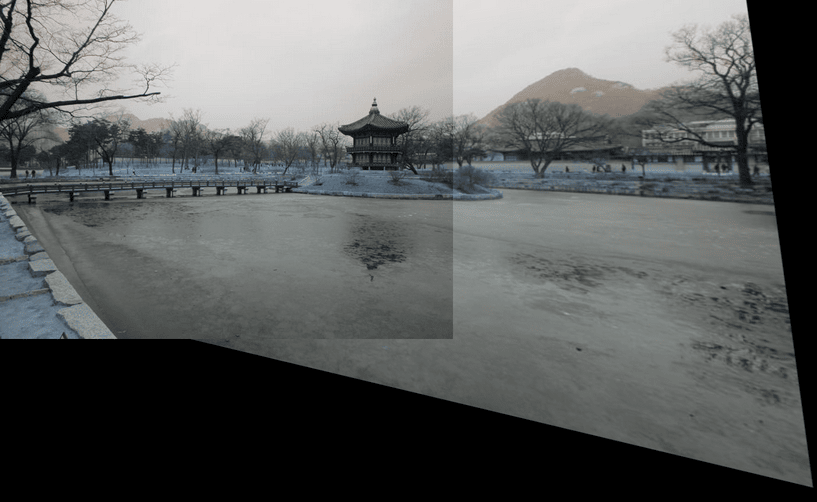
Brief Overview
In this problem set, you will implement panoramic stitching. Given two input images, we will “stitch” them together to create a simple panorama. To construct the image panorama, we will use concepts learned in class such as keypoint detection, local invariant descriptors, RANSAC, and perspective warping.
The panoramic stitching algorithm consists of four main steps which we ask you to implement in individual functions:
Detect keypoints and extract local invariant descriptors (we will be using ORB) from two input images.
Match the descriptors between the two images.
Apply RANSAC to estimate a homography matrix between the extracted features.
Apply a perspective transformation using the homography matrix to merge image into a panorama.
Functions to implement (refer to function comments for more detail):
get_orb_features(2 points)match_keypoints(2 points)find_homography(2 points)transform_ransac(2 points)panoramic_stitching(2 points)
Getting started
Run the following code to import the modules you’ll need.
%matplotlib inline
import cv2
import random
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from google.colab.patches import cv2_imshow
%%capture
! wget -O img1.jpg "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1omMydL6ADxq_vW5gl_1EFhdzT9kaMhUt"
! wget -O img2.jpg "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=12lxB1ArAlwGn97XgBgt-SFyjE7udMGvf"
Visualize Input Images
img1 = plt.imread('img1.jpg')
img2 = plt.imread('img2.jpg')
def plot_imgs(img1, img2):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 20))
for a in ax:
a.set_axis_off()
ax[0].imshow(img1)
ax[1].imshow(img2)
plot_imgs(img1, img2)

(a) Feature Extraction
(i) Compute ORB Features
def get_orb_features(img):
'''
Compute ORB features using cv2 library functions.
Use default parameters when computing the keypoints.
Hint: you will need cv2.ORB_create() and some related functions
Input:
img: cv2 image
Returns:
keypoints: a list of cv2 keypoints
descriptors: a list of ORB descriptors
'''
#############################################################################
# TODO #
#############################################################################
orb = cv2.ORB_create()
keypoints, descriptors = orb.detectAndCompute(img, None)
#############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#############################################################################
return keypoints, descriptors
(ii) Match Keypoints
def match_keypoints(desc_1, desc_2, ratio=0.75):
'''
Compute matches between feature descriptors of two images using
Lowe's ratio test. You may use cv2 library functions.
Hint: you may need to use cv2.DescriptorMatcher_create or cv2.BFMatcher
and some related functions
Input:
desc_1, desc_2: list of feature descriptors
Return:
matches: list of feature matches
'''
#############################################################################
# TODO #
#############################################################################
matchingAlgorithm = cv2.BFMatcher()
matches = matchingAlgorithm.knnMatch(desc_1,desc_2, k=2)
good_matches = []
for i,j in matches:
if i.distance < ratio*j.distance:
good_matches.append(i)
#############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#############################################################################
return good_matches
kp_1, desc_1 = get_orb_features(img1)
kp_2, desc_2 = get_orb_features(img2)
kp_img1 = cv2.drawKeypoints(img1, kp_1, None, color=(0,255,0), flags=0)
kp_img2 = cv2.drawKeypoints(img2, kp_2, None, color=(0,255,0), flags=0)
print('keypoints for img1 and img2')
plot_imgs(kp_img1, kp_img2)
keypoints for img1 and img2

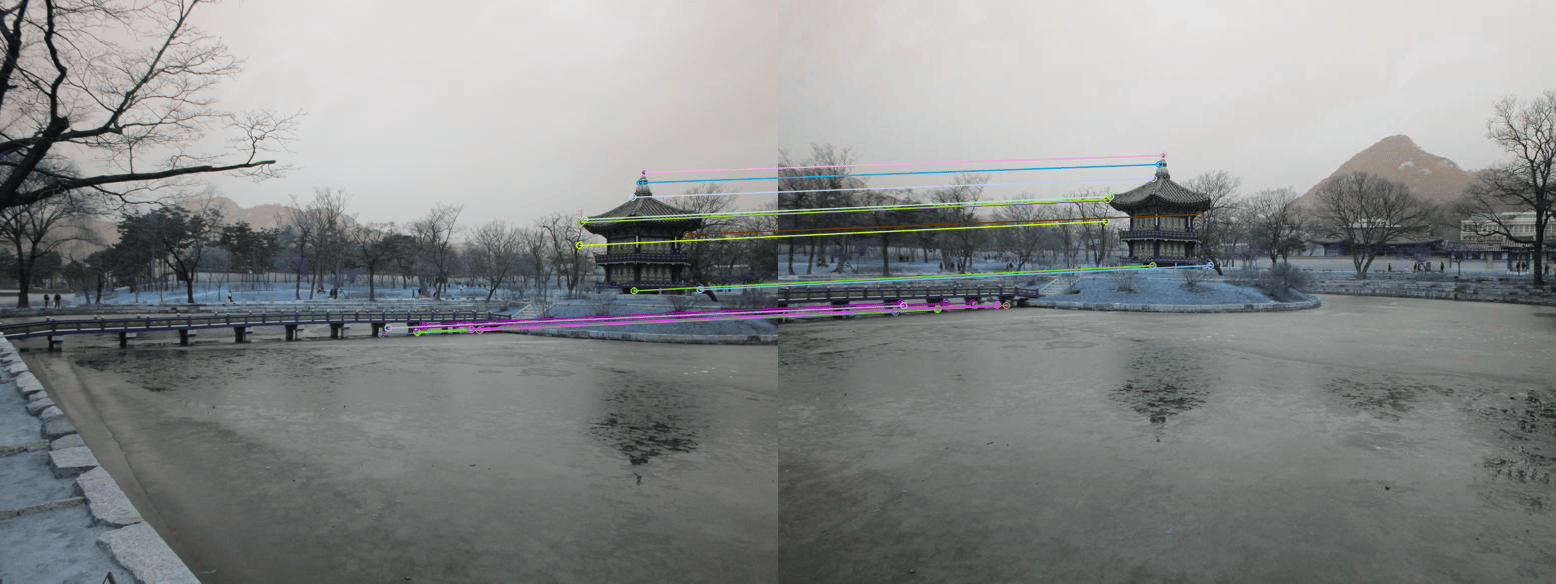
matches = match_keypoints(desc_1, desc_2)
match_plot = cv2.drawMatches(img1, kp_1, img2, kp_2, matches[:20], None, flags=2)
print("orb feature matches")
cv2_imshow(match_plot)
orb feature matches

(b) Find Homography Matrix
def find_homography(PTS2, PTS1):
'''
Use either nonlinear least squares or direct linear transform
to find a homography that estimates the transformation mapping from pts_1
to pts_2.
e.g. If x is in pts_1 and y is in pts_2, then y = H * x
Hint if using nonlinear least square:
The objective function to optimize here is:
||pts_1 - cart(H*homog(pts_2))||^2 where homog(x) converts x into
homogeneous coordinates and cart(x) converts x to cartesian coordinates.
You can use scipy.optimize.least_squares for this.
Hint if using direct linear transform:
The solution is given by the right-singular vector with the smallest singular value in the singular vector decomposition.
You can use np.linalg.svd for this.
Input:
pts_1, pts_1: (N, 2) matrix
Return:
H: the resultant homography matrix (3 x 3)
'''
#############################################################################
# TODO #
#############################################################################
N = PTS2.shape[0]
A = np.zeros((2*N, 9))
for i in range(N):
x1, x2 = PTS1[i,0], PTS2[i,0]
y1, y2 = PTS1[i,1], PTS2[i,1]
A[2*i] = np.array([-x1, -y1, -1, 0, 0, 0, x1*x2, y1*x2, x2])
A[2*i+1] = np.array([0, 0, 0, -x1, -y1, -1, x1*y2, y1*y2, y2])
_, _, V = np.linalg.svd(A)
H = np.reshape(V[-1], [3, 3] )
#############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#############################################################################
return H
(c) Implement RANSAC
def transform_ransac(x1, x2, verbose=False):
'''
Implements RANSAC to estimate homography matrix.
Hint: Follow the RANSAC steps outlined in the lecture slides.
Hint: Try num iterations = 1000 (not mandatory)
Hint: Threshold ε =2 (ε here refers to the L2 distance between two points)
Input:
pts_1, pts_1: (N, 2) matrices
Return:
best_model: homography matrix with most inliers
'''
#############################################################################
# TODO #
#############################################################################
epsilon = 2.0
iterations = 2000
batch_size = 4
N = x1.shape[0]
bestInlier = 0
best_inlierSet = []
for i in range(iterations):
idx = random.sample(range(N), k=batch_size)
batch_1 = x1[idx,:]
batch_2 = x2[idx,:]
H = find_homography(batch_2, batch_1)
inlierSet = []
for i in range(N):
pt1 = np.append(x1[i,:],1).T
pt2 = np.append(x2[i,:],1).T
new_pt2 = np.dot(H, pt1)
new_pt2 = new_pt2 / new_pt2[2]
if np.linalg.norm(new_pt2 - pt2) < epsilon:
inlierSet.append(i)
if len(inlierSet) > bestInlier:
bestInlier = len(inlierSet)
best_inlierSet = inlierSet
final_PTS1 = x1[best_inlierSet,:]
final_PTS2 = x2[best_inlierSet,:]
best_model = find_homography(final_PTS2, final_PTS1)
#############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#############################################################################
return best_model
(d) Panoramic Stitching
def panoramic_stitching(img1, img2):
'''
Given a pair of overlapping images, generate a panoramic image.
Hint: use the functions that you've written in the previous parts.
Input:
img1, img2: cv2 images
Return:
final_img: cv2 image of panorama
'''
#############################################################################
# TODO #
# 1. detect keypoints and extract orb feature descriptors #
# 2. match features between two images #
# 3. compute homography matrix H transforming points from pts_2 to pts_1. #
# Note the order here (not pts_1 to pts_2)! #
#############################################################################
kp_1, desc_1 = get_orb_features(img1)
kp_2, desc_2 = get_orb_features(img2)
matches = match_keypoints(desc_1, desc_2)
PTS1 = np.zeros([len(matches),2])
PTS2 = np.zeros([len(matches),2])
i = 0
for match in matches:
PTS1[i,:] = kp_1[match.queryIdx].pt
PTS2[i,:] = kp_2[match.trainIdx].pt
i = i + 1
H = transform_ransac(PTS2,PTS1)
#############################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#############################################################################
# apply perspective wrap to stitch images together
final_img = cv2.warpPerspective(img2, H, (img2.shape[1] + img1.shape[1], img2.shape[0] * 2))
final_img[0:img1.shape[0], 0:img1.shape[1]] = img1
return final_img
result = panoramic_stitching(img1, img2)
cv2_imshow(result)

